“Sitting
Sitting is the opposite of standing
Sitting is the opposite of running around
Sitting is a wonderful thing to do”
@brianjordanalvarez SITTING 🗣️🗣️🗣️🎶🎶🎶
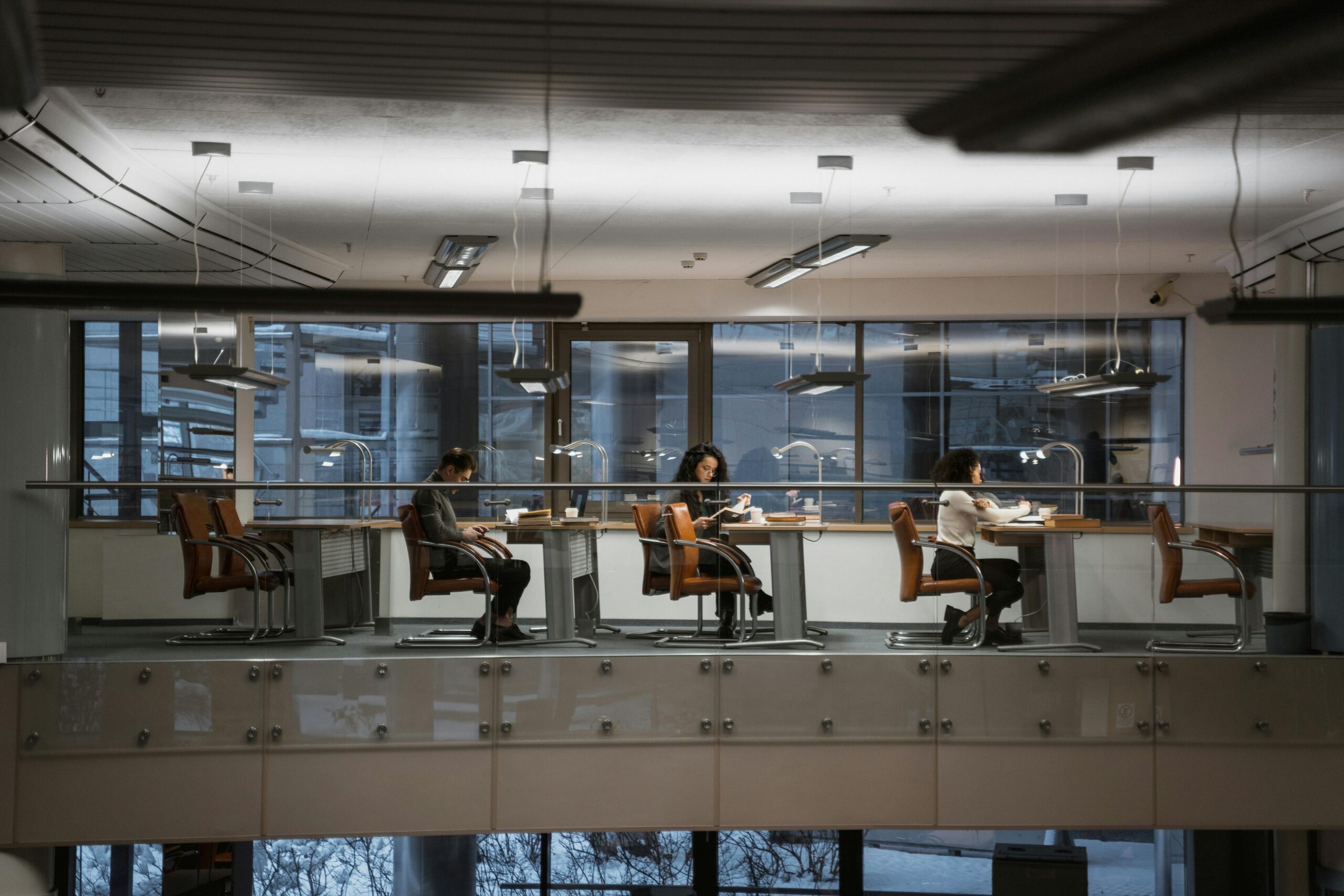
As Particle’s resident editor, I do a lot of sitting.
The above wise words from TJ Mack have become a mantra of sorts, repeated most mornings as I settle in to reading emails and media releases.
But new research led by Dr Christian Brakenridge from Swinburne University of Technology has made me question my relationship to my ergonomic office chair.
The findings, published in the journal Diabetologia in April 2024, propose the optimal lengths of time one should spend sitting, standing and running around each day.
Apparently, I should be doing a lot less sitting and perhaps some more hanging from a barbell if I want to keep my risk of heart disease and diabetes in check.
SITTING IS THE OPPOSITE OF RUNNING AROUND
The Swinburne team used data from a study in the Netherlands, where researchers attached sensors to the thighs of 2388 adult participants. They tracked measures of cardiometabolic health and glycaemic control markers (an indicator of diabetes risk).
The team also used the activity monitor data to understand how people divided their time between sitting, standing, light-intensity physical activity, moderate to vigorous physical activity (some may say running around) and sleeping.
From this information, using newly developed analysis techniques, the team could work out averages for the optimum amounts of each of these activities in a 24-hour period.
According to the study, the ideal day is composed of 6 hours of sitting, 5 hours and 10 minutes of standing, 2 hours and 10 minutes each of light-to-moderate and moderate-to-vigorous physical activity and 8 hours and 20 minutes of sleep.
While the chart looks intense, co-author Genevieve Healy, a professor of physical activity and health at University of Queensland, says it’s important to consider the day holistically.
“The critical thing is to consider the whole 24-hour day and how you’re spending your time between all of those behaviours.”
She went on to explain that the study is part of a global shift in the way we talk about physical activity and health – from treating behaviours like exercise in isolation to looking at your time as a whole.
“We used to have recommendations for how much sleep you should get and how much activity you should do, and now it’s like, hang on! We have 24 hours in the day, and they’re all linked together.”
The new study contributes to a growing pool of empirical data about how people spend their time and how this correlates to health outcomes. As Genevieve says, “You need to be able to measure the whole day to be able to form these guidelines.”
SITTING IS SOMETHING THAT PEOPLE SAY IS BAD
In physical activity and health research, sitting is used as a shorthand for sedentary behaviour. A 2019 narrative review published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine identifies two high-profile studies in 1999 and 2005 that first measured time spent in this awake but inactive state.
Earlier studies used time spent in front of the TV for a similar purpose. While this captures people’s use of their leisure time, sitting expands the focus to include hours spent working and commuting.
Claims about the dangers of sitting are serious and shocking. The phrase “sitting is the new smoking”, first published in a Runner’s World article in 2013, gets a lot of mileage, including on Australian Government websites.
In a 2014 phone interview with the LA Times, Dr James Levine of the Mayo Clinic famously said, “Sitting is more dangerous than smoking, kills more people than HIV and is more treacherous than parachuting. We are sitting ourselves to death.”
Although Levine, who invented the treadmill desk, perhaps stands to benefit from sitting’s bad press, research published in January 2024 backs up the seriousness of the problem. Sitting was found to increase a person’s risk of straight up dying from any cause by 16%.
As well as death, further research has expanded the list of concerns to include heart disease, obesity, diabetes, dementia, varicose veins, back pain and cancer.
EASY CHANGES
Recommendations to help individuals avoid the health risks of excess sitting range from the reasonable to the extreme.
On the benign end of the scale, advice that would be at home in a weight loss brochure or on a motivational DVD abounds. “Try taking the stairs!” “Do a lap of your living room every time there’s an ad break!”
One particularly bizarre routine had me concerned I would ever be able to finish writing an article. The 20-8-2 breakdown is recommended by Alan Hedge, Professor of Ergonomics at Cornell University.
The numbers refer to how one should subdivide each hour at work: sit for 20 minutes, stand for 8 minutes and then move for 2 minutes. Hedge suggests using an egg timer or phone alarm at work to remind you. Hopefully your co-workers don’t mind.
Before you embark on a gruelling, day-long, sit-stand-walk pomodoro, it’s worth considering other factors at play.
WHY ARE YOU NOT STANDING UP RIGHT NOW?
Genevieve agrees that there’s small behavioural changes that people can make but points out that, in many circumstances, individuals aren’t able to make healthy choices.
Call centre workers, for example, have deadlines and expectations that keep them on the phones and therefore seated at their desks.
“What you can do as an individual is actually quite constrained by your job tasks and your job demands.”
Alongside her research, Genevieve is the lead on a project called BeUpStanding that aims to improve the health and wellbeing of desk-based workers by introducing solutions at an organisational level.
She points to the value of socio-ecological models of behaviour change that take into account all the environmental, social and cultural motivators of an individual’s behaviour.
These could include factors like building layouts and safety concerns, missing infrastructure or workplace culture. It can be challenging to be the only one standing in a meeting or going for a walk at lunchtime.
The BeUpStanding program is free for workplaces to access and utilises workplace champions to be role models for healthy behaviours.
Teams are empowered to choose what strategies to implement and how to address the unique challenges of their workplace and give them ownership to shape their experience.
So while the idea of subdividing your time according to a pie chart may be daunting, it’s best to take it as something to be aware of as opposed to a personal prescription.
Sometimes, you deserve to sit.
@monicamoniquemartin Ben and I were both moved to tears the first time we heard TJ Mack perform his song “Sitting”. He penned something so rare, so potent, and so so giving — made medicine of melody, and healed something we may never have been able to name. To be alive while he shares his gift is nothing short of a miracle. Thank you so much TJ Mack, I hope our rendition of this classic brings even a fraction of the joy you’ve brought us. @brianjordanalvarez #sitting #oppositeofstanding #youdeservetosit #somethinglikeanap #botoc #wife #sittim